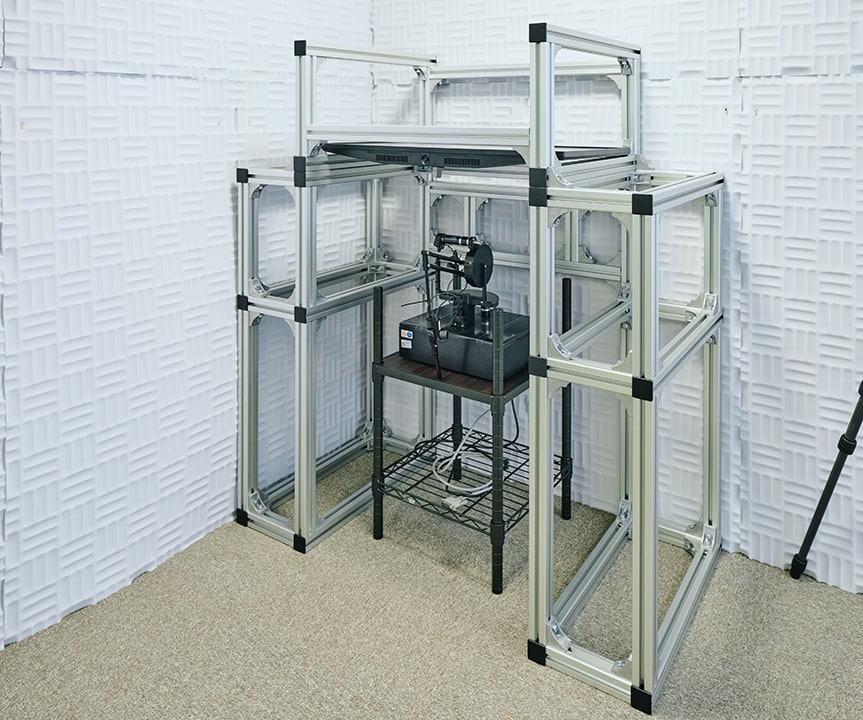
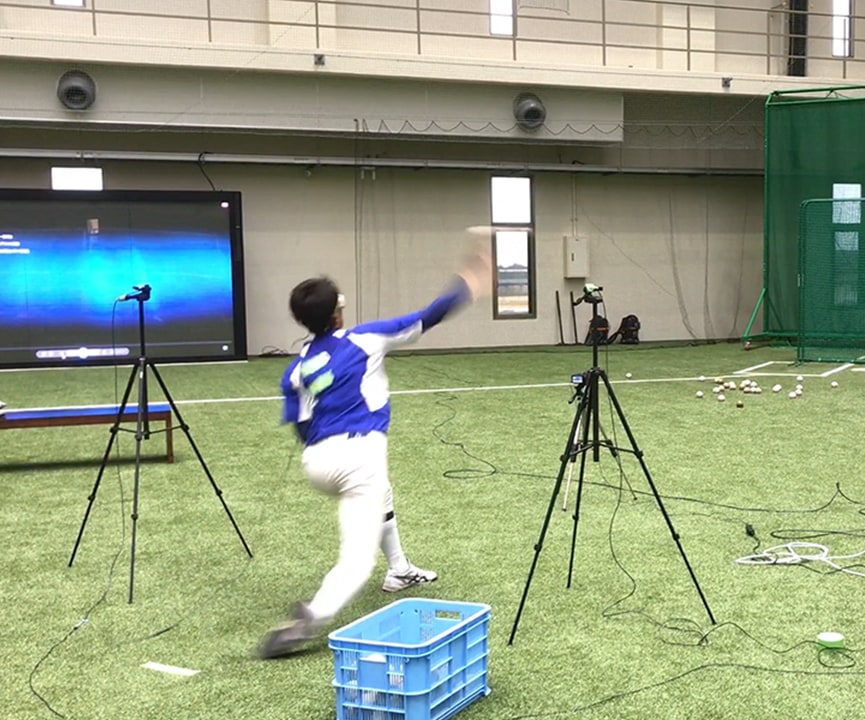
MOTOR CONTROL & LEARNING
APPROACH
アプローチ

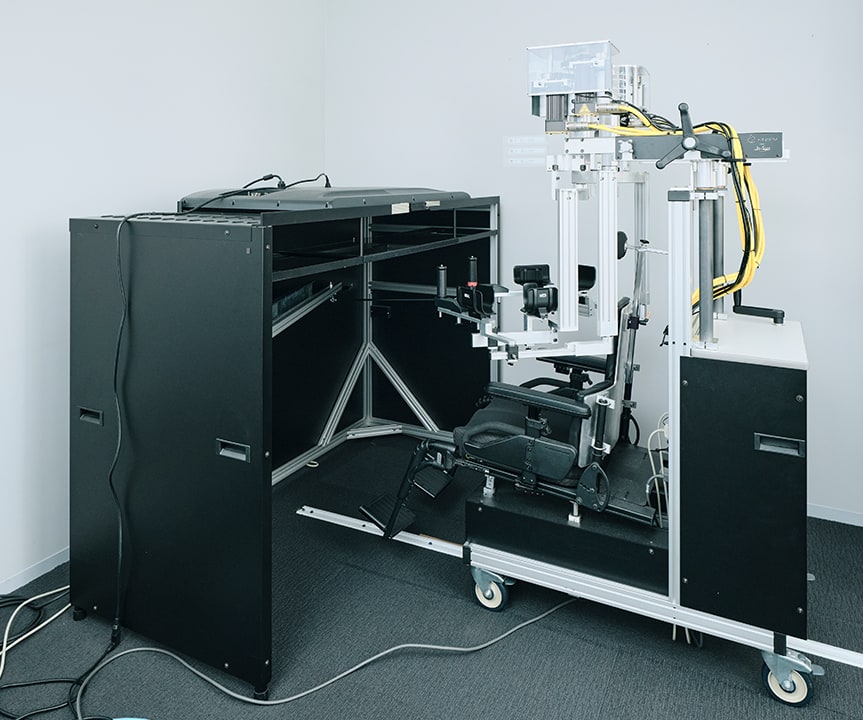
運動システムがどのような要因によって
どのように変化するのか?
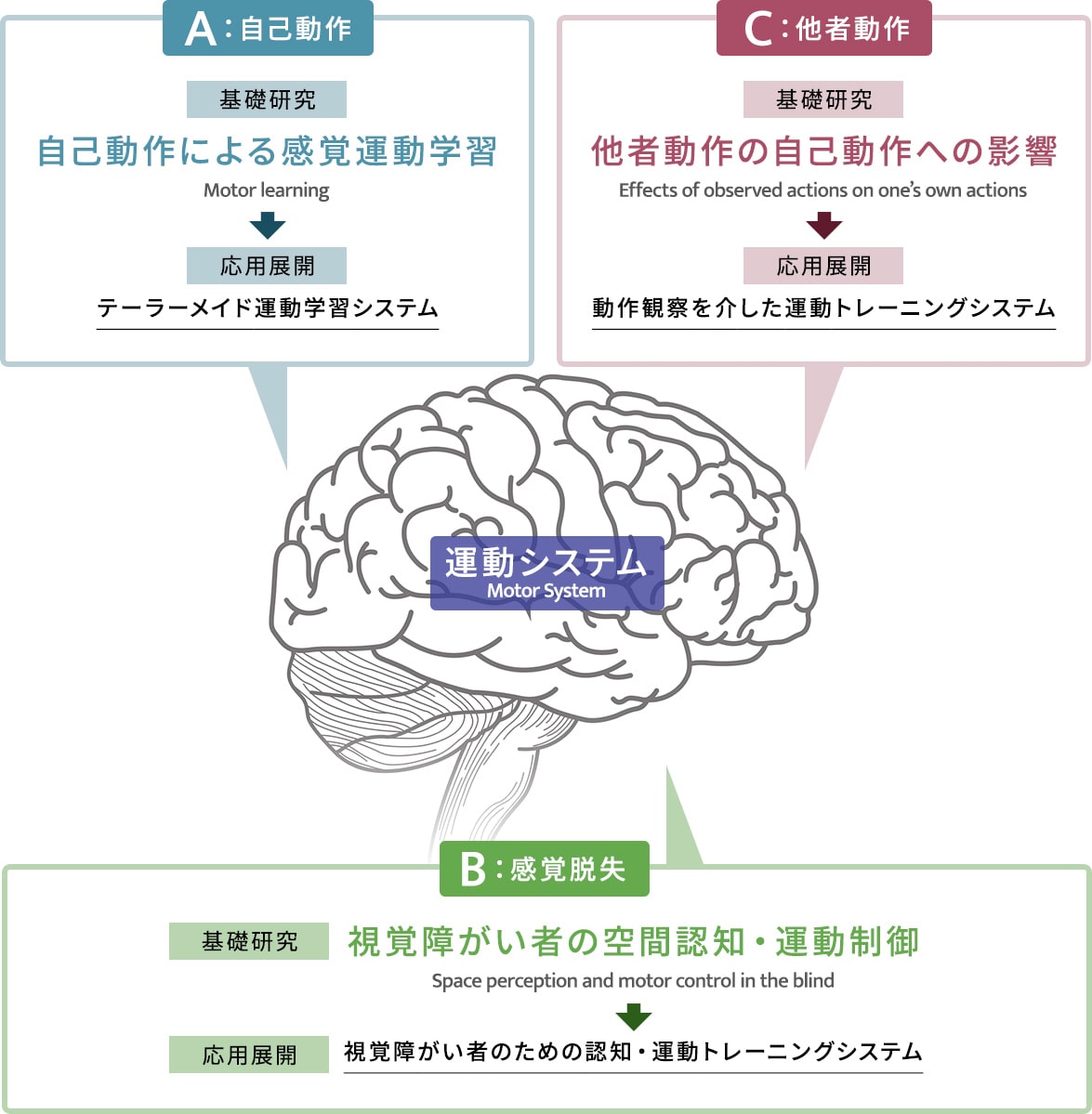
自己動作による運動学習
Motor learning
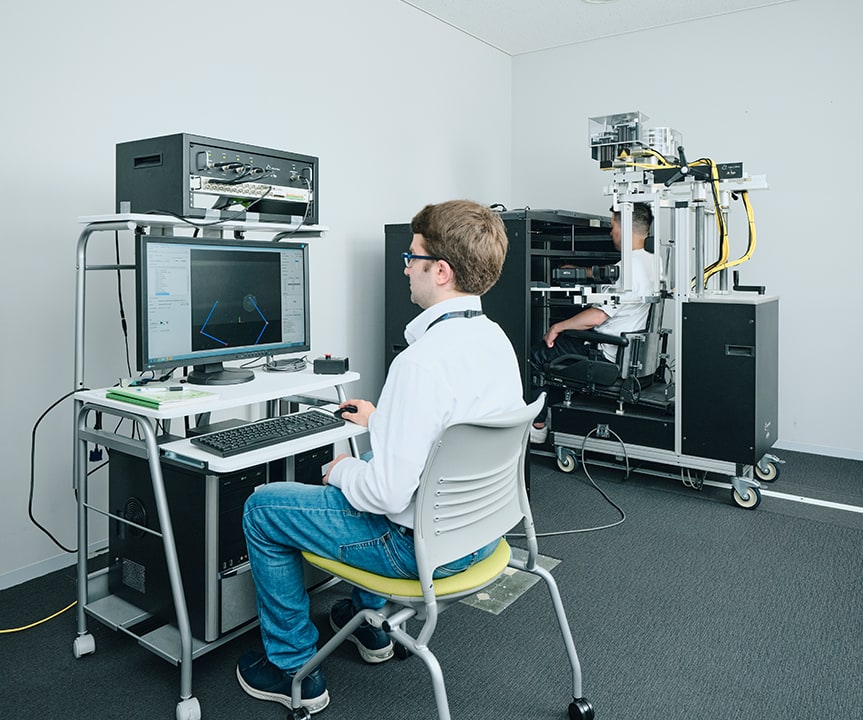
新しい運動技能を獲得するためには、新しい運動記憶を脳内に形成する必要です。脳は、どのような感覚情報を利用して、どのような計算機序で運動記憶を脳内に表現しているのでしょうか?
- Hierarchical motor adaptations negotiate failures
during force field learning
T Ikegami, G Ganesh, TL Gibo, T Yoshioka, R Osu, M Kawato
PLoS Computational Biology 17 (4), e1008481, 2021 - Intermittent visual feedback can boost motor learning
of rhythmic movements: evidence for error feedback beyond cycles
T Ikegami, M Hirashima, R Osu, D Nozaki
Journal of Neuroscience 32 (2), 653-657, 2012 - Asymmetric transfer of visuomotor learning between
discrete and rhythmic movements
T Ikegami, M Hirashima, G Taga, D Nozaki
Journal of Neuroscience 30 (12), 4515-4521, 2010
視覚障がい者の空間認知・運動制御
Space perception and motor control in the blind
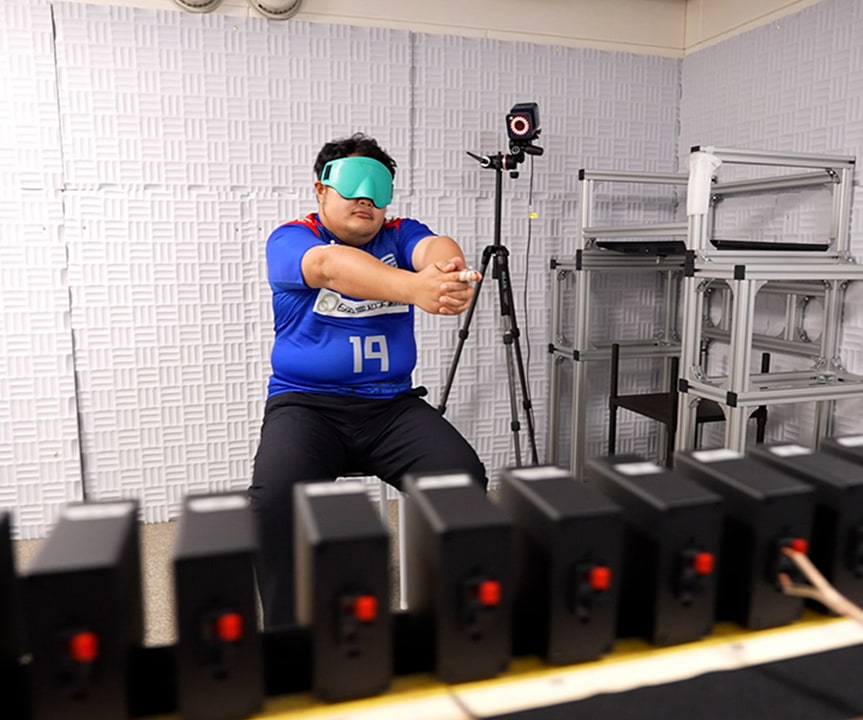
ブラインドサッカー選手のような視覚障がい者アスリートは、目が見えていると錯覚するほど巧みで正確な運動パフォーマンスを発揮することができます。視覚に頼ることなく、脳はどのようにして正確な空間認知や身体制御を実現しているのでしょうか?
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the occipital
cortex interferes with foot movements in acquired but not congenitally blind
individuals.
T Ikegami, G Miura, M Hirashima, E Naito, S Hirose in submission
他者動作の自己動作への影響
Effects of observed actions on one’s own actions
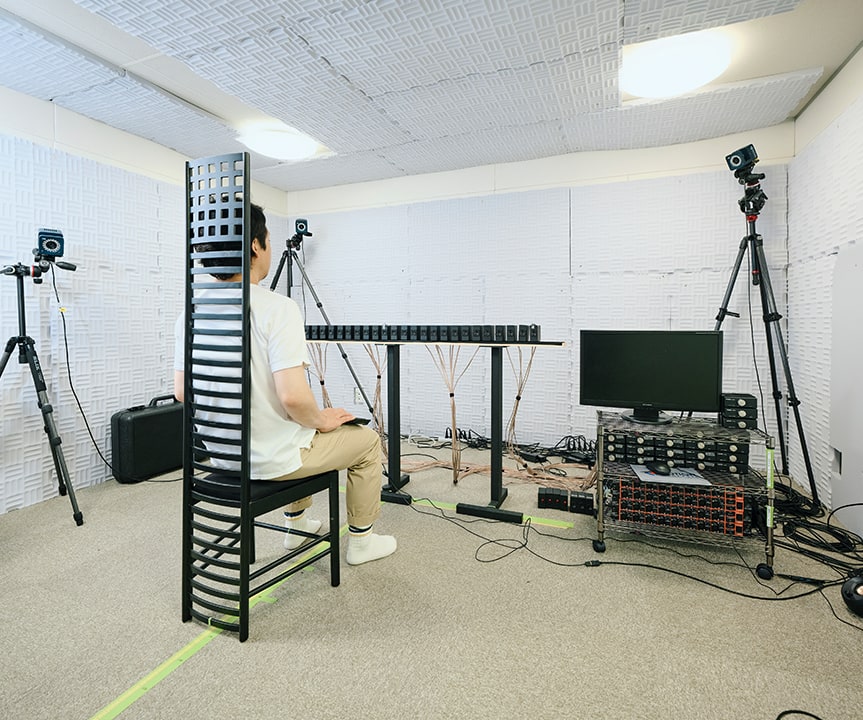
誰かと握手をしたりダンスを踊ったり、社会生活を営む上で、運動を介した他者とのコミュニケーションは不可欠です。脳は、どのようにして相手の動作を早く正確に予測し、他者の動作の目的や意図を理解しているのでしょうか?
- Prediction error induced motor contagions in human
behaviors
T Ikegami, G Ganesh, T Takeuchi, H Nakamoto
eLife 7, e33392, 2018 - Shared mechanisms in the estimation of self-generated
actions and the prediction of other’s actions by humans
T Ikegami, G Ganesh
eNeuro 4 (6) ENEURO.0341, 2017 - Watching novice action degrades expert motor
performance: causation between action production and outcome prediction of
observed actions by humans
T Ikegami, G Ganesh
Scientific Reports 4 (1), 6989, 2014