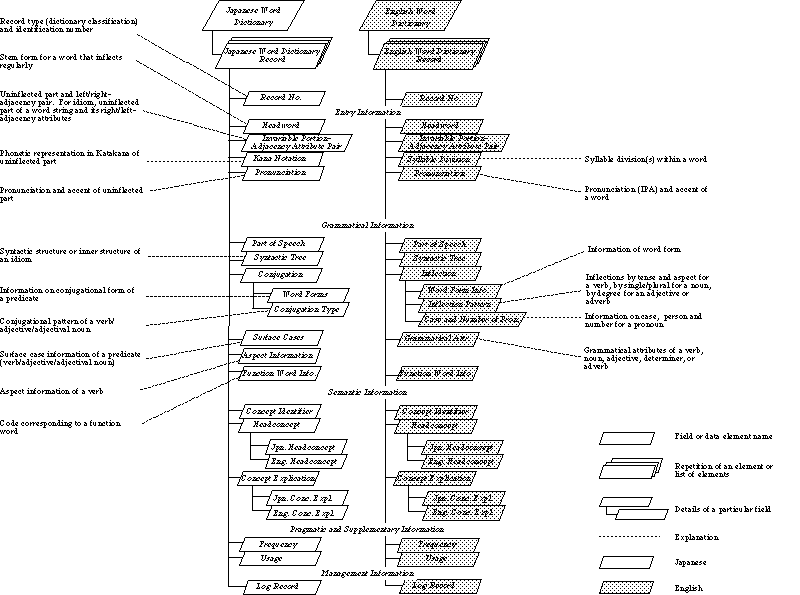
Entry information consists of the headword, the portion of the word that is invariable during inflection, the adjacency attribute pair, pronunciation, and kana notation for the Japanese Word Dictionary and in the English Word Dictionary, syllable division. The headword describes the root form of a word when it inflects regularly or the inflected form if it has an irregular inflection. Words that don't inflect are described as they are.
The invariable portion of a headword is the string of characters that is common to all the inflected forms of the word, and is not necessarily the word stem. This term is used synonymously with 'morpheme' in this document. Adjacency attributes are symbols that indicate the morphological restrictions on the adjacent words or morphemes in a sentence. Kana notation and pronunciation in the Japanese Word Dictionary and syllable division and pronunciation in the English Word Dictionary are given for single-word entries. The kana notation provides the reading for each of the kana-kanji written notation for the invariable portion of the headword. When inputting a word, this information can be used in kana-kanji conversion in word processing. In the English Word Dictionary, the syllable division is described and provides information for hyphenation. Pronunciation information provides information that can be used for speech synthesis, and is described with katakana and stress symbols in the Japanese Word Dictionary, and in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) for the English Word Dictionary.
Grammatical information in the Japanese Word Dictionary consists of the part of speech, a syntactic tree, conjugation, surface cases, aspect information, and function word information. In the English Dictionary, the part of speech, a syntactic tree, inflection, grammatical attributes, and function word information are provided. The information provided in the grammatical information section can be used to find the syntactic structure of a sentence in syntactic analysis, or to determine the sentence structure during syntactic generation. A syntactic tree is provided for word entries that consist of more than one word. In the Japanese Word Dictionary, function word information is provided for particles, auxiliary verbs, formal nouns, numerals, and conjunctions. In the English Word Dictionary, it is provided for prepositions, auxiliary verbs, coordinate conjunctions, subordinate conjunctions, conjunctive adverbs, relative pronouns, relative adverbs, interrogative pronouns, interrogative adverbs, and their equivalents. In the Japanese Word Dictionary, information on conjugation is provided for predicates (verbs, adjectives, adjectival nouns) and auxiliary verbs, and information on surface cases is provided for predicates. Aspect information is provided for verbs. In the English Word Dictionary, inflection information is provided for verbs, nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, and inflectional endings. Grammatical attributes show the grammatical behavior of verbs, nouns, adjectives, adverbs, and determiners.
The semantic information consists of concept identifiers. Headconcept and concept explications are provided as accompanying information. The concept identifier is a numerical expression and provides information on concepts, the basic constituent of the Concept Dictionary. It is provided in order to preserve the identity of a concept in its various relations. The headconcept is a representative word that is the most appropriate in expressing the concept identified by the concept identifier. The concept explication is an explanation written in natural language for the purpose of assisting humans in differentiating one concept from another. The concepts are similar to word senses in paper-based dictionaries, and provide the information necessary to discriminate meanings of words. Unlike paper-based dictionaries, these concepts are language independent. Every word dictionary record has a concept identifier to link the Word Dictionary and the Concept Dictionary.
The pragmatic and supplementary information consists of usage and frequency. This information can be used for likelihood evaluation in sentence analysis and generation.