情報利活用基盤研究室 > トピックス
情報利活用基盤研究室 > 研究紹介 > サイバーフィジカルクラウドコンピューティング
情報利活用基盤研究室 > 構成員
情報利活用基盤研究室 > 研究業績
情報利活用基盤研究室 > 各種資料
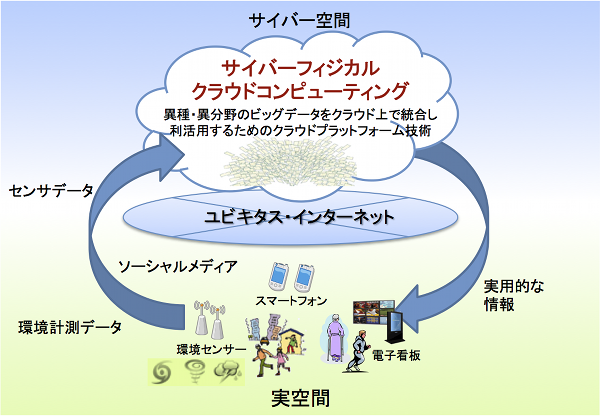
サイバーフィジカルクラウドコンピューティング
ユビキタスコンピューティングの発展に伴い、現実社会におけるさまざまな環境計測データや、個人の発信するソーシャルメディア情報などが大量にネットワーク上を流れています。本研究室では、実世界に埋め込まれた様々なセンサーからのデータを「取って」「繋いで」「貯めて」「使う」ためのプラットフォームを実現するために、多種多様なフィジカルデータをクラウドサーバー上で蓄積し、それらをサイバー空間上で統合して解析・利用できるようにするプラットフォーム技術について研究開発を行っています。つまり、実空間のセンサーから得られる地域の局所的な環境の変化に合わせ、Webやソーシャルメディアから社会的な影響を広範囲かつ網羅的に取得します。ソーシャルメディアを通じて異常な出来事が通報されると、これに連動して対象地域のセンサーから動的に環境情報を取得しながらリモートから状況を把握できるように実用的な情報を提供します。まず医療情報と災害関連情報とを具体的なアプリケーションターゲットとして、クラウドプラットフォームの構築、データ管理手法や解析技術の開発、データフォーマットの標準化などに取り組むことを計画しております。
サイバーフィジカルクラウドコンピューティング ホワイトペーパー:A Vision of Cyber-Physical Cloud Computing for Smart Networked Systems
要旨:
This report is the initial outcome of a joint project between the National Institute of Information and Communication Technology (NICT), Japan and the U.S. National institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). A team of researchers from both organizations collaborated to conceive the Cyber-Physical Cloud Computing (CPCC) architectural framework presented in this report. One of the motivating factors for this research was the earthquake and tsunami that hit Japan in March 2011 and the resulting damage. The magnitude of the Japanese earthquake and tsunami highlighted the importance of a robust and reconfigurable disaster recovery systems. Recent advances in information technology provide an opportunity to create smart networked systems for power grids, transportation, and healthcare systems that will enhance existing disaster management solutions. Smart networked systems and societies will result from the emerging network of people, intelligent devices, and mobile personal computing and communication devices (mPCDs).
There are five technologies that are core to the concept of a Smart Networked Systems and Societies (SNSS): 1) networked computer systems, 2) real-time systems, 3) wireless sensor/actuator networks, 4) social networks and, 5) cloud computing services. A CPCC architectural framework -- defined as “a system environment that can rapidly build, modify and provision auto-scale cyber-physical systems composed of a set of cloud computing based sensor, processing, control, and data services” -- integrates the characteristics of CPS and cloud computing into a single framework, and is a first step in achieving the SNSS vision.
The CPCC architectural framework supports the realization of an SNSS and the appropriate services to users and applications at the appropriate place and the appropriate time via the appropriate devices. This framework supports the deployment of large-scale and data- intensive systems, involving complex distributed decision-making. The benefits of the CPCC framework include: efficient use of resources, modular composition providing customizability, rapid development and scalability, smart adaptation to environment, scalable reliability, resiliency, and performance based on user needs.
The report describes two component systems developed at NICT in Kyoto, Japan that serve examples of existing systems that can easily be modified to support the concepts described in the CPCC architecture framework. The systems are: CPSenS (an information technology platform for on-demand integration of real-world sensing information with cyber cloud systems) and K-L Grid (an information service development platform for utilizing big data).
In conclusion, this report identifies challenges and research areas that need to be addressed to realize the CPCC architectural framework. The research areas include: the virtualization of sensors and actuators, interconnectivity between CPCC services, data integration, knowledge generation, resource orchestration, security, privacy, performance, reliability, resiliency, and metrology.