GOSAT-GW is the third satellite in the GOSAT Series for observations of greenhouse gases, and it is planned to be launched in 2024 fiscal year. GOSAT-GW challenges to observe CO2 and methane, as well as air pollutant nitrogen dioxide (NO2) from space.
We, NICT, develop the data processing system to derive NO2 concentration with high accuracy and high speed.
GOSAT-GW Mission
The Global Observing SATellite for Greenhouse gases and Water cycle (GOSAT-GW) is an Earth observation satellite that performs the greenhouse gases observing satellite mission and the water cycle change observation mission. To accomplish each mission, GOSAT-GW carries two sensors: the Total Anthropogenic and Natural emissions mapping SpectrOmeter 3 (TANSO-3) and the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer 3 (AMSR3).
The greenhouse gases observing satellite mission is being implemented jointly by the Ministry of the Environment, the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES), and Japan Aerospace eXploration Agency (JAXA) in accordance with the Basic Plan on Space Policy. NICT has signed a joint research agreement with NIES and the Japan Agency for Marine-earth Science and TEChnology (JAMSTEC) to conduct NO2 observation research using TANSO-3.
Why NO2 is measured
CO2 released into the atmosphere has the effect of raising the temperature of the earth. A large amount of CO2 is emitted from places where support human economic activity, such as power plants and factories. The Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports that there is no doubt that the effects of human activities have caused the atmosphere, oceans, and land to warm. In order to maintain economic activity while protecting the global environment, we must first understand where greenhouse gases, including CO2, are being emitted from and how much of them are being emitted.
Here we have to consider the atmospheric lifetime of CO2 (how long it remains in the atmosphere without disappearing). Since the lifetime of CO2 is very long, ranging from several years to several decades, CO2 is once released, then transferred with air currents. Even if the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere is measured, it is difficult to identify where and how much CO2 is emitted.
Therefore, we measure NO2. NO2 is emitted simultaneously with CO2 from power plants and factories, and the NO2 lifetime in the atmosphere is short, ranging from a few hours to a few days. By measuring the NO2 concentration with CO2 simultaneously, it is possible to estimate the CO2 emissions at that location with high accuracy. TANSO-3 will be the first satellite in the GOSAT series to attempt to observe NO2.
Measure planes, not spots
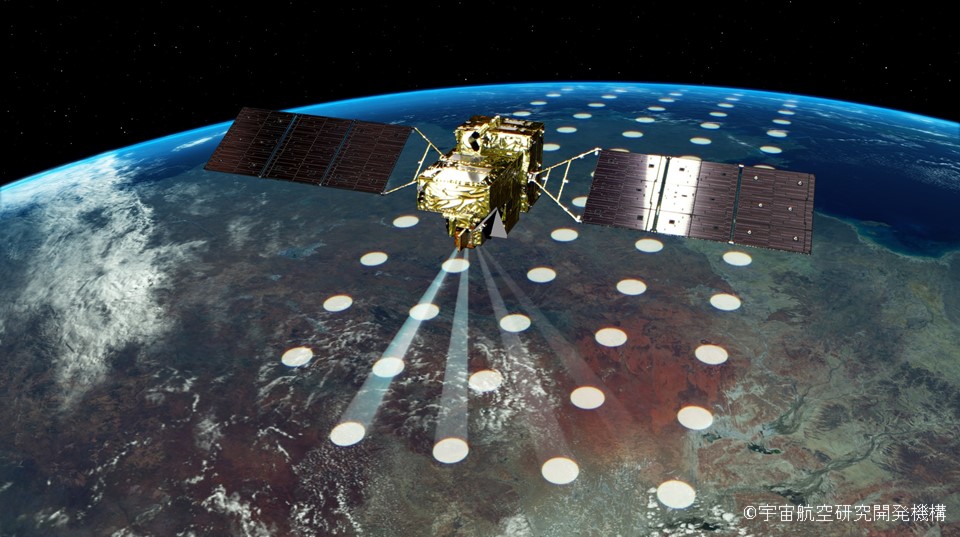
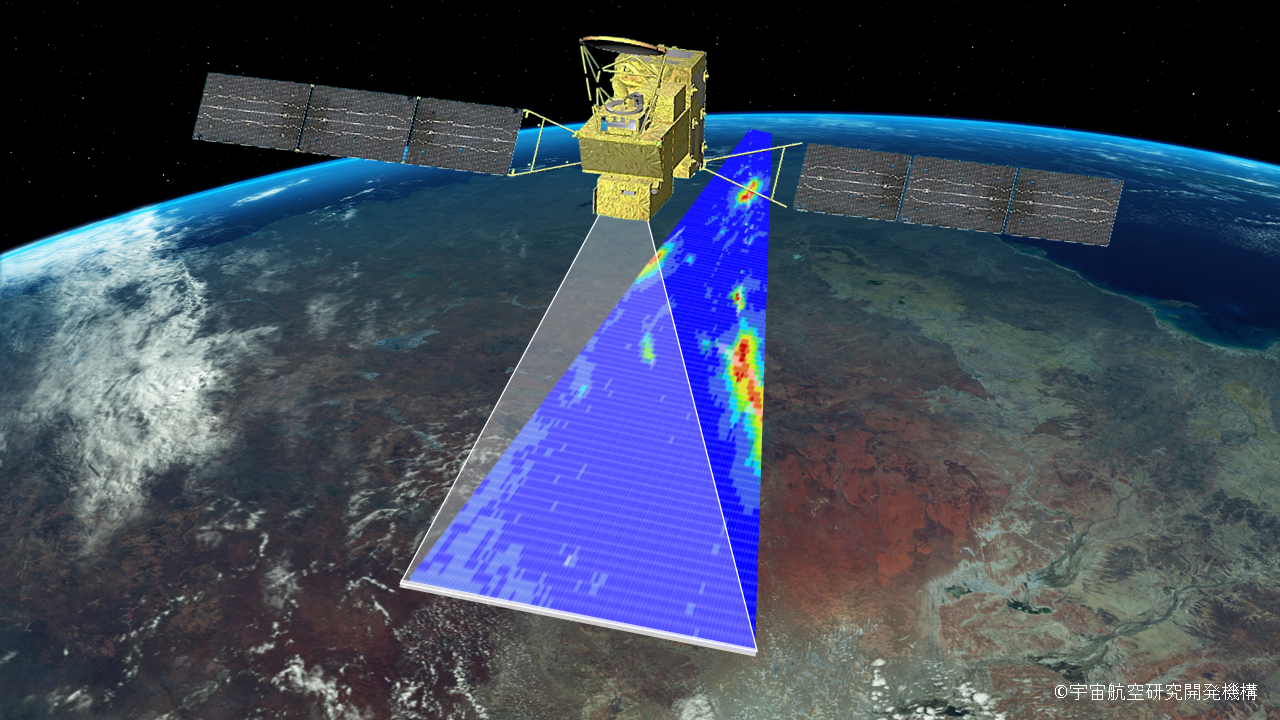
GOSAT-GW is a first for the GOSAT series in that it will use a grating-type spectrometer.
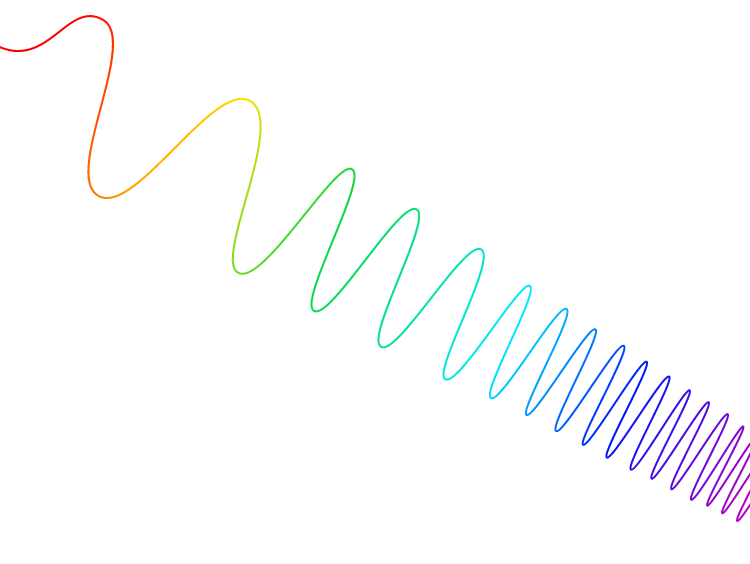
The GOSAT series successfully launched the GOSAT satellite in 2009 and the GOSAT-2 satellite in 2018, and the sensors on these satellites used a Fourier transform spectrometer. This spectrometer has the advantage of high wavelength resolution, but as shown in Figure 1, each observation point is not adjacent to another, but is observed as a spot. On the other hand, GOSAT-GW, which uses a diffraction grating spectrometer, observes as a plane as shown in Figure 2. If we compare the observation to the act of painting, GOSAT and GOSAT-2 drip paint from above with a dropper, while GOSAT-GW paints it solidly with a brush. This allows us to capture the size and shape of the NO2 plume (smoke flow) emitted from a factory chimney, for example. This is a great advantage in estimating emissions.

Calculate accurately, and fast
Using a grating-type spectrometer means that the number of observation points will increase compared to using a Fourier transform spectrometer. In the case of GOSAT-GW, the number of observation points is expected to increase by more than 100 times by those of GOSAT or GOSAT-2, so data processing will need to be not only accurate but also fast.
One of the largest error sources in deriving the vertical column concentration of NO2 from the spectrum acquired by the TANSO-3 sensor is the Air Mass Factor (AMF). The AMF is a value obtained by normalizing the optical path length of the observed light, with the optical path length when the light reaches the earth's surface vertically from the top of the atmosphere set to 1. This AMF can be calculated using a radiative transfer model that formulates the physical processes such as scattering and absorption of radiation propagating through the atmosphere.
However, radiative transfer models generally have high computational costs, and it is unrealistic to run the radiative transfer model on all of the observational data observed by GOSAT-GW. It is necessary to improve the calculation speed of AMF calculations using the radiative transfer model while maintaining accuracy.
We, NICT, have developed a unique algorithm incorporating machine learning to calculate AMF, achieving both high calculation accuracy and speed. As a result, we have succeeded in improving calculation accuracy by approximately 12 times and speed by approximately 2 times compared to conventional methods.
For universities, companies, and government agencies
Thank you for your interest in our research.
We collaborate with domestic and international companies, public research institutes, and universities. We actively engage in joint research, the provision of technology and data, and outreach activities such as lectures.
If you can cooperate with us, we will enter into a joint research agreement or a contracted research agreement. We will prepare the documents necessary for specific collaboration, such as a confidentiality agreement for consultations at the previous stage.
We have failed many times up until now, but have been able to learn from those failures and use them to advance to the next stage. This could not have been achieved without the support of many people. Once again, we would like to express our deepest gratitude.
We hope that you will also make use of the "methods" and "results" that we have obtained. If you are interested in our research, please feel free to contact us.
Contact:
Terahertz Laboratory, Terahertz Technology Research Center, NICT
Senior Researcher
Tomohiro Sato
Email: tosato@nict.go.jp / Phone: 042-327-7033
NEWS:
Link:
Ministry of the Environment